|
Silicon Solar Cells & Antireflection Coating |
|||||
Laser Annealing
Nanopaticle Stacks
(INC) method
Silicon Solar Cells & Antireflection Coating Nanoparticles Nanoimprint & Nanofabrication Organic Solar Cells Carbon Nanotube |
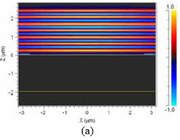
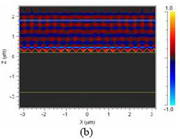
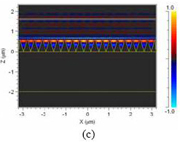
Optical Optimization of Solar Cells The development of highly efficient solar cells is one solution to the problems of energy depletion and environmental destruction. The key issue when attempting to increase the external quantum efficiency of semiconductor-based solar cells is reducing interfacial reflection in the solar cell working-wavelength regime. In addition, the reflectance decreased upon increasing the height of the pyramidal features. From simulations, we predicted that the reflectance would be reduced to less than 1% when the pyramidal features had a height of 500 nm; in contrast, cylindrical pillars having the same period and height would not reduce the reflectance to less than 10%. From an analysis of the pyramidal structures using the three-dimensional FDTD method, we found that the reflection of light in the near field could also be reduced dramatically by a pyramidal structure having a height of 500 nm; this finding is similar to the result simulated by the rigorous coupled-wave analysis.
|
Simulated reflectance spectra of |
|||
Copyright(c) 2008 Nano-optpelectronics Lab., Department of Material Science and Engineering, National Taiwan University No. 1, Sec. 4, Roosevelt Road, Taipei, 10617 Taiwan(R.O.C) Phone:+886-2-3366-4076 Fax:+886-2-2362-7651 |
|||||